If you have any symptoms of ovarian cancer, they need to be checked by your doctor.
How is ovarian cancer diagnosed?
If you have any ovarian cancer symptoms, get checked by your doctor as soon as possible.
Your doctor may suggest several tests and scans to check for cysts, tumours or other changes.
These tests may include:
Physical examination
Your doctor checks your body. This will involve feeling your tummy from the outside and an internal pelvic examination.
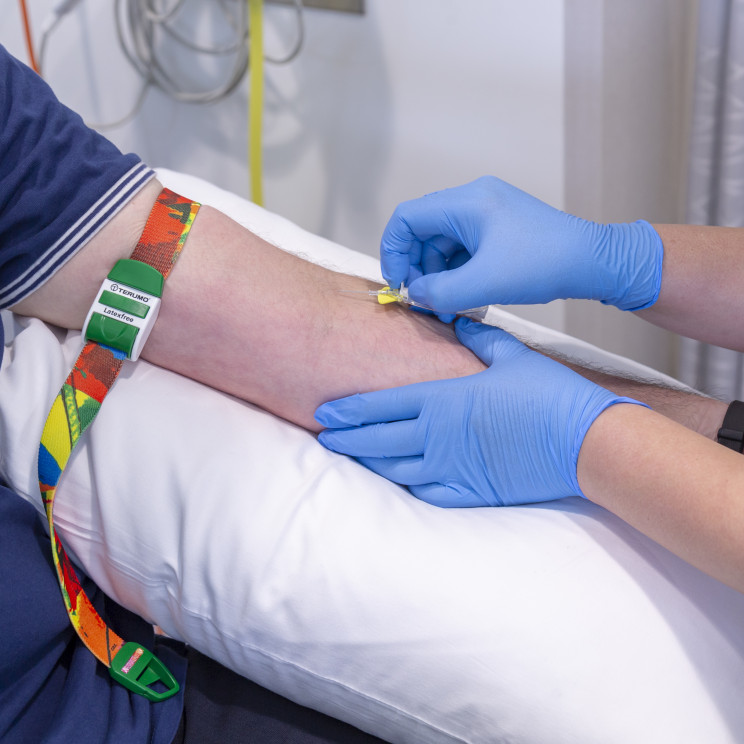
Blood tests
A blood sample is taken.
Colonoscopy
A specialist looks at the entire length of your large bowel by gently inserting a long, flexible tube through your anus and rectum into your colon.
CT scan
A CT scan creates a 3D picture of the inside of your body. It can show smaller cancers than an x-ray and enlarged lymph nodes.
Ultrasound scan
An ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create pictures of the inside of your body.
PET-CT scan
A PET-CT scan uses a radioactive dye injected into your arm that will show up in areas affected by cancer. You may have to travel for this scan.
Cervical smear tests will not show ovarian cancer.
After a diagnosis
If your test results show cancer, this can be a difficult time, and feelings can change from one moment to the next.
Everyone reacts differently when they learn they have cancer. There is no right or wrong way to feel.
Talk about your treatment options with your doctor, family and friends. Ask for as much information as you need. It is up to you how involved you want to be in decisions about your treatment.
Stages of ovarian cancer
The ovarian cancer stage tells you the cancer's size and if it has spread to other parts of your body.
Based on your test results, the treatment team will give the cancer a stage between 1 to 4.
In general, the higher the number, the more the ovarian cancer has spread in your body.
| Stage | Definition |
| Stage 1 | Cancer is found in one or both ovaries. |
| Stage 2 | Cancer is in one or both ovaries and has spread to other organs in the pelvis. |
| Stage 3 |
Cancer is in one or both ovaries and has spread to the abdomen's lining, the bowel or lymph nodes in the abdomen or pelvis. |
| Stage 4 |
Cancer is in one or both ovaries and has spread further, to the inside of the bladder or rectum, throughout the abdomen or to other body parts. |
Staging helps your cancer treatment team recommend the best treatment for you.
Prognosis for ovarian cancer
The prognosis is the likely outcome of a disease.
If the test results show ovarian cancer, you may wish to speak with your treatment team about the prognosis.
The doctors will look at the type and stage of the cancer as well as your age and general health to give a prognosis, but no doctor can predict the exact outcome for you.

Treatment for ovarian cancer includes surgery, chemotherapy and, sometimes, radiation treatment.

We are here to help and support you and your whānau through cancer diagnosis, treatment and recovery…

How you can be open and honest with your family/whānau and friends about your cancer diagnosis.
We know that going through cancer is tough and can raise many questions. You are not alone.
We have health professionals to answer your questions and provide the support you need.
Get in touch
